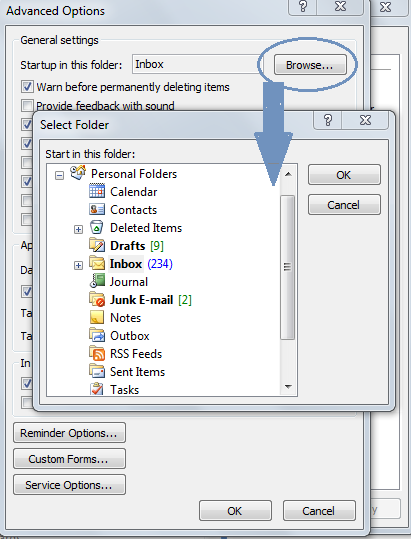
- Change The Startup Folder In Outlook 365 Email
- Change The Startup Folder In Outlook 365 Download
- Change The Startup Folder In Outlook 365 Free
- Change The Startup Folder In Outlook 365 Online
Microsoft Office Applications save your files to OneDrive by default since the February 2019 Office 365 update. If you always save your documents on to your CentreStack Cloud Drive then you may want to change the default save location in Microsoft Office. There are multiple ways to change the default save location in Word, Excel & PowerPoint. In Outlook: Right-click Inbox in the left pane and select New Folder. Type a name, and press Enter. On Outlook.com: Select New Folder at the bottom of your folder list in the left pane, type a name, and press Enter. To make categories in Outlook, Home Categorize All Categories; online, select a message, then Categorize Manage categories.
Topics Map > Features and Functionality > Client Capabilities > Web (OWA)
By default, messages that are sent to you are stored in your Inbox. But you can organize your messages into a hierarchical folder system and adjust it as your needs change. You can access Outlook on the web using any supported browser.
Default folders
Your account starts with these default folders:
- Inbox Incoming messages arrive in your Inbox unless you've created an Inbox rule to redirect them to another folder, or they're identified as junk email.
- Drafts If you create or respond to a message, but can't finish it right away, it will automatically be saved to your Drafts folder. You can come back to the message later to continue editing it, and then send it.
- Sent Items By default, a copy of every message you send is put in your Sent Items folder.
- Deleted Items When you delete a message, it's moved to the Deleted Items folder.
- Junk Email Messages that have junk email characteristics but that aren't blocked by a spam filter before they reach your mailbox will automatically be moved to this folder. Learn about junk email and phishing has more information about your Junk Email folder.
- Notes This is a read-only folder. You must use Outlook to create or edit items in this folder.
- Clutter Clutter helps you move low priority messages out of your Inbox so that you can easily scan for important messages. Learn more.
You may see other folders that have been created by your administrator. Note: default folders cannot be renamed/deleted.
Right-click menu for folders
Most of what you can do with a folder will be found in the right-click menu. Actions you can take include:
- Create new folder Use this to create a new subfolder in the folder you right-clicked.
- Rename Rename the folder. You can't rename the default folders, such as the Inbox folder.
- Delete Delete the entire folder. Delete will move the folder to the Deleted Items folder.
- Empty Deletes everything in the folder, including any subfolders.
- Add to Favorites Adds the current folder to your Favorites.
- Move Opens a window where you can select a folder to move this folder to. You can also move a folder by clicking it and dragging it to where you want it.
- Mark all as read Marks every item in the folder as read.
- Assign policy This feature may not be available to you. If it is, you can use it to assign a retention or archive policy to messages in the folder.
Creating folders
You can create additional folders to organize your messages any way you want. For example, you can create a folder for a specific project, or for all messages sent by a particular person, or all messages sent to a distribution group that you're a member of.
To create a new folder, right-click the parent folder you want to create the new folder in. If you want a top-level folder (a folder at the same level as your Inbox), you would use your mailbox as the parent folder.
To create a folder:
- Right-click on your account.
- Click create new folder.
- Type the name you want to use for this folder.
- Press Enter or click away.
Important Note: It is recommended you not create sub-folders under your Inbox.
Moving folders
There are two ways to move a folder.
- Click the folder you want to move and drag it to where you want it - this action can only be used when moving the folder to a sub-folder - you cannot move it with the intention of sorting the folder listing (sorting is preset and cannot be overwritten).
- Right-click the folder you want to move and click Move.
A window will pop up that you can use to choose what folder to move the folder into. Click the folder you want to move to and click Move. Or click Cancel to close the move folder window without moving the folder.
- You can even create a new folder to move the subfolder into by right-clicking the parent folder you want and clicking Create new subfolder.
Important considerations when managing folders/emails
- A folder (including all emails) can only be moved to another location. It cannot be copied.
- When moving/copying folders/emails to another location, or downloading a large mailbox, be patient. There may be times when you will need to wait a certain amount of time before the move/copy completes. Important: Do not quit out of the application until you have verified the move/copy command has completed. Review following Microsoft resources:
- If you want to move/copy a sub-set of emails to another location, you can use the CTRL or Shift-click actions to select the desired email messages. Note: During our testing, we have noticed inconsistencies when attempting to use CTRL or Shift-click actions to select the desired email messages. If the range of messages you are attempting to select is large, you may not be able to select them. You will need to select a smaller range of messages.
- When scrolling through a folder with a large number of messages, the web client may require some time to show you the messages within the folder listing. Please be patient.
The Deleted Items folder
When you delete a message, it's first moved to the Deleted Items folder. You can either let messages stay there, or you can set Outlook on the web to automatically empty your Deleted Items folder when you sign out. Your administrator may have set up a policy to empty items from your Deleted Items folder after they've been there for a preset number of days. For example, there may be a policy that removes anything that's been in your Deleted Items folder for 30 days.
Recover deleted items
If your administrator has enabled the recover deleted items feature, you can use it to recover items that have been deleted from your Deleted Items folder. How long items will be recoverable depends on settings that are controlled by your administrator.
- Right-click Deleted Items.
- Click Recover deleted items.
- Select all item you want and then click Recover. The item will be moved to its default location. Messages will go to your Inbox, calendar items will go to your Calendar, contacts to your Contacts folder, and tasks to your Tasks folder.
You can also select Purge to permanently delete an item. If you purge an item, you won't be able to use Recover deleted items to get it back. Purging a message won't remove it from any backups that were made before you purged it.
Change The Startup Folder In Outlook 365 Email
Favorites
It's not unusual to end up with so many folders that it can be hard to keep track of the folders that are most important to you. To make it easier to keep track of those folders, you can add them to your Favorites. Favorites don't appear in your folder list until you've added at least one folder to Favorites. Adding a folder to Favorites doesn't move the folder, but creates a link to it.
- To add a folder to Favorites, right-click it and click Add to Favorites.
- You can re-order folders in Favorites by clicking and dragging, or by right-clicking and then clicking Move up in list or Move down in list.
- To remove a folder from Favorites, right-click it in Favorites and click Remove from Favorites. This only removes the link to the folder from Favorites; it won't delete the folder from your mailbox.
What else do I need to know?
- The folders you create can be at the same level as your default folders, for example, the Inbox or Sent Items folders. Or, you can create sub-folders within any existing email folder. It is recommended you not create sub-folders under your Inbox.
- You may need to refresh your browser to view a folder that you just created in the folder list.
- If you want to create a personal information folder as a subfolder to a mail folder, you can create the folder and then move it to the location you want. Some folders, for example, the Inbox, can't be moved to another location.
- Some folders, for example, the Inbox, can't be renamed. If the folder can't be renamed, the Rename option in the menu will appear dimmed.
- After you delete a folder, it's moved to the Deleted Items folder. The folder isn't permanently removed until you empty the Deleted Items folder or delete the folder from the Deleted Items folder.
Note
Office 365 ProPlus is being renamed to Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise. For more information about this change, read this blog post.
Important

This article contains information about how to modify the registry. Make sure to back up the registry before you modify it. Make sure that you know how to restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up, restore, and modify the registry, see Description of the Microsoft Windows registry.
Summary
This article describes various methods that you can use to reset user options and registry settings in Microsoft Office Word.
There are two basic types of options that you can define in Word:
- Options that affect the way that the program operates. The information for this kind of option is generally stored in the Microsoft Windows registry.
- Options that affect the formatting or the appearance of one or more documents. The information for this kind of option is stored in templates or documents.
When you troubleshoot unusual behavior in the program or a document, first determine whether the problem might be caused by formatting, options, or settings. If the behavior occurs in multiple documents, we recommend that you try to reset Microsoft Word to the program's default settings.
How to reset user options and registry settings in Word
Warning
Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly by using Registry Editor or by using another method. These problems might require that you reinstall your operating system. Microsoft cannot guarantee that these problems can be solved. Modify the registry at your own risk.
To manually reset a registry key, you must first delete it.
Important
Always export a registry key before you delete it. This step is important because you may have to restore the functionality that's provided by the key.
- Exit all Microsoft Office programs.
- Open Registry Editor.
- Locate and select the registry key that you want to delete. Refer to the Main locations of Word settings in the Windows Registry section.
- Select File > Export, type a file name for the backup copy of the key, and then click Save.
- Make sure that the key that you just exported is selected, and then click Delete on the Edit menu.
- When you are prompted to respond to one of the following messages, click Yes:
- Are you sure you want to delete this key?
- Are you sure you want to delete this key and all of its subkeys?
- Exit Registry Editor.
After you delete a registry key and restart the program, Word runs the Setup program to correctly rebuild the registry key. If you want to rebuild the registry key before you run the program, repair your installation by following the steps in Repair an Office application.
More Information
Main locations of Word settings in the Windows Registry
You can reset some Word settings, such as the Word Data and Options keys in the Windows registry.
Word key
Word for Microsoft 365, Word 2019, and Word 2016
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice16.0Word
Word 2013
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice15.0Word
Word 2010
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice14.0Word
The Data and Options key are the most frequently changed areas.
Data key
Word for Microsoft 365, Word 2019, and Word 2016
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice16.0WordData
Word 2013
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice15.0WordData
Word 2010
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice14.0WordData
This key contains binary information for 'most recently used' lists, including the most recently used file list and the most recently used address book list. This key also contains 'Track Changes' settings and 'Edit' settings.
Options key
Word for Microsoft 365, Word 2019, and Word 2016
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice16.0WordOptions
Word 2013
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice15.0WordOptions
Word 2010

HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice14.0WordOptions
This key stores the options that you can set from Microsoft Word.
Change The Startup Folder In Outlook 365 Download
The options are in two groups: default options and optional settings. Default options are established during the setup process. You can change them by modifying options in Word. These options may or may not appear in the registry.
Wizards key
Word for Microsoft 365, Word 2019, and Word 2016
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice16.0WordWizards
Word 2013
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice15.0WordWizards
Word 2010
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice14.0WordWizards
All wizard defaults are stored in this key. These settings are created the first time that you run a wizard.
Common key
Word for Microsoft 365, Word 2019, and Word 2016
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice16.0Common
Word 2013
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice15.0Common
Word 2010
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftOffice14.0Common
This key is used by other Microsoft programs, such as the Office programs. These settings are shared between programs. Changes made in one program's settings also appear in the other program's settings.
Shared Tools key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftShared Tools
This key contains the paths for all Windows utilities. (The path may include utilities such as Equation, WordArt, and MS Graph.) Paths for graphics filters and text converters are also registered in this location.
Templates and add-ins
Global Template (Normal.dotm)
To prevent formatting changes, AutoText entries, and macros that are stored in the global template from affecting the behavior of Word and documents that are opened, rename your global template (Normal.dotm). Renaming the template lets you quickly determine whether the global template is causing the issue.
When you rename the Normal.dotm template in Word 2007 or later, you reset several options to the default settings. These options include custom styles, custom toolbars, macros, and AutoText entries. We strongly recommend that you rename the template instead of deleting the Normal.dotm template. If you determine that the template is the issue, you will be able to copy the custom styles, custom toolbars, macros, and AutoText entries from the Normal.dotm template that's renamed.
Certain types of configurations may create more than one Normal.dotm template. These situations include cases where multiple versions of Word are running on the same computer or cases where several workstation installations exist on the same computer. In these situations, make sure that you rename the correct copy of the template.
To rename the global template file, follow these steps:
Exit all Office programs.
Open Command Prompt.
Run the following command:
ren %appdata%MicrosoftTemplatesNormal.dotm OldNormal.dotm
When you restart Word, a new global template is created that contains the Word default settings.
Add-ins (WLLs) and templates in the Word and Office Startup folders
When you start Word, the program automatically loads templates and add-ins that are located in the Startup folders. Errors in Word may be the result of conflicts or problems with an add-in.
To determine whether an item in a Startup folder is causing the problem, you can temporarily empty the folder. Word loads items from the Office Startup folder and the Word Startup folder.
To remove items from the Startup folders, follow these steps:
Exit all instances of Word, including Microsoft Outlook if Word is set as your email editor.
Open the Office startup folder.
Right-click one of the files that's contained in the folder, and then click Rename.
After the file name, type .old, and then press Enter. Note the original name of the file. You may have to rename the file by using its original name.
Start Word.
If you can no longer reproduce the problem, you have found the specific add-in that causes the problem. If you must have the features that the add-in provides, contact the vendor of the add-in for an update.
If the problem isn't resolved, rename the add-in by using its original name, and then repeat steps 3 through 5 for each file in the Startup folder.
If you can still reproduce the problem, open the
%AppData%MicrosoftWordSTARTUPfolder.Repeat steps 3 through 5 for each file in this Startup folder.
COM add-ins
Change The Startup Folder In Outlook 365 Free
COM add-ins can be installed in any location, and they are installed by programs that interact with Word.
To view the list of COM add-ins in Word, see View, manage, and install add-ins in Office programs.
If add-ins are listed in the COM Add-Ins dialog box, temporarily turn off each add-in. To do so, clear the check box for each listed COM add-in, and then click OK. When you restart Word, Word doesn't load the COM add-ins.
Change The Startup Folder In Outlook 365 Online
Summary of Word options and where they are stored
In the following table, 'Template' refers to either the Normal.dotm template or a custom template.
| Setting name | Storage location |
|---|---|
| AutoCorrect-Formatted text | Normal.dotm |
| AutoCorrect-Shared entries | .ACL files user.acl |
| AutoSave path | Registry |
| AutoText | Template |
| Company name | Winword.exe |
| Custom keystroke assignments | Template |
| Font substitution | Registry |
| Macros | Template/document |
| Picture editing | Registry |
| Print data forms | Document |
| Snap to grid | Registry |
| Styles | Template/document |
| Toolbars | Template/document |
| User info | Registry |
| View toolbars | Template |
| View/toolbar | Template |
| Document Parts | Template |
AutoCorrect lists are shared between Office programs. Any changes that you make to the AutoCorrect entries and settings when you are in one program are immediately available to the other programs. Additionally, Word can store AutoCorrect items that are made up of formatted text and graphics.
Information about AutoCorrect is stored in various locations. These locations are listed in the following table.
| AutoCorrect information | Storage location |
|---|---|
| AutoCorrect entries shared by all programs | .ACL file in the %appdata%MicrosoftOffice folder |
| AutoCorrect entries used only by Word (formatted text and graphics) | Normal.dotm |
| AutoCorrect settings (correct two initial capitals, capitalize names of days, replace text as you type) | Registry |
| AutoCorrect settings used only by Word (corrects accidental usage of CAPS LOCK key, capitalizes first letter of sentences) | Registry |